Family Immigration: Understanding Your Path to Residing in the United States
Discover the pathways, eligibility criteria, and step-by-step guide to family immigration in the U.S. Keep your family united with expert insights on petitions and visas.

Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Family immigration focuses on keeping families united in the U.S.
- Immediate relatives have no numerical limitations on visas, while family preference categories do.
- A two-step petition process is required for family-based immigration.
- Challenges include documentation gaps and financial requirements.
- Consulting with professionals can streamline the immigration process.
Table of contents
- Understanding Family Immigration
- Eligibility and Pathways
- Immigration Petition and Filing Process
- Immigration with Family: Considerations and Best Practices
- Immigration to the United States Through Family Channels
- Role of U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS)
- Conclusion and Next Steps
- Frequently Asked Questions
**Family immigration** is the process through which foreign nationals obtain permanent residency in the United States based on their familial relationships with U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents. This pathway is vital as it reaffirms the commitment of U.S. immigration policy to keep families united. Family-based immigration, immigration with family, and the immigration petition processes play crucial roles in this endeavor, ensuring that families can reunite and thrive together in the U.S.
In this blog post, we will delve into the various pathways and eligibility criteria associated with immigration to the United States for families, as well as the role of the United States immigration services in this process.
Understanding Family Immigration
Family immigration refers to the sponsorship of relatives through a legally binding relationship that permits them to secure permanent residence in the United States. Unlike employment-based immigration, family immigration focuses solely on kinship as the basis for immigration eligibility.
A U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident, known as the petitioner, files a formal petition with the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) on behalf of their relative, known as the beneficiary. This sponsorship bureaucratically establishes the familial connection that allows for immigration.
Under the family-based immigration option, eligible U.S. citizens and lawful permanent residents can sponsor specific relatives for Green Cards. One of the most significant benefits of immigration with family is that it provides a pathway to obtaining lawful permanent resident status, which grants individuals the right to reside and work indefinitely in the United States.
For an in-depth understanding of family immigration, you can refer to resources like Understanding Family Immigration.
Eligibility and Pathways
When considering family immigration, it's essential to understand the eligibility criteria and the distinct categories of family members that can be sponsored for immigration.
Immediate Relatives
Immediate relatives of U.S. citizens can immigrate without numerical restrictions, meaning there is no cap on the number of visas available each fiscal year. Categories include:
- Spouses
- Unmarried children under age 21
- Parents (the petitioner must be at least 21)
- Siblings (with a 21-year age requirement for the petitioner)
This makes immediate relatives the fastest path for immigration, as their applications are processed without quota limits. For more on immediate relatives, visit Family Immigration Overview.
Family Preference Categories
In contrast, family preference visas have annual limits and are subject to quotas:
- F1: Unmarried children age 21 or older of U.S. citizens
- F3: Married children of U.S. citizens
- F4: Siblings of U.S. citizens
- F2A: Spouses and unmarried children under 21 of lawful permanent residents
- F2B: Unmarried children age 21 or older of lawful permanent residents
Lawful permanent residents have more limited options and can only petition for spouses and unmarried children. More details can be found on the eligibility overview resource here.
Key Eligibility Requirements for Sponsors
Sponsoring family members requires the following criteria:
- Must be at least 18 years of age (or 21 for parents and siblings)
- Must be a U.S. citizen or lawful permanent resident
- Must reside in the United States
- Must demonstrate the ability to financially support the family member through an Affidavit of Support
For more information on the eligibility requirements, refer to Key Eligibility Requirements. For additional resources on immigration law, please see Immigration Official Resources.
Immigration Petition and Filing Process
The Two-Step Process
The immigration petition process is a two-step procedure:
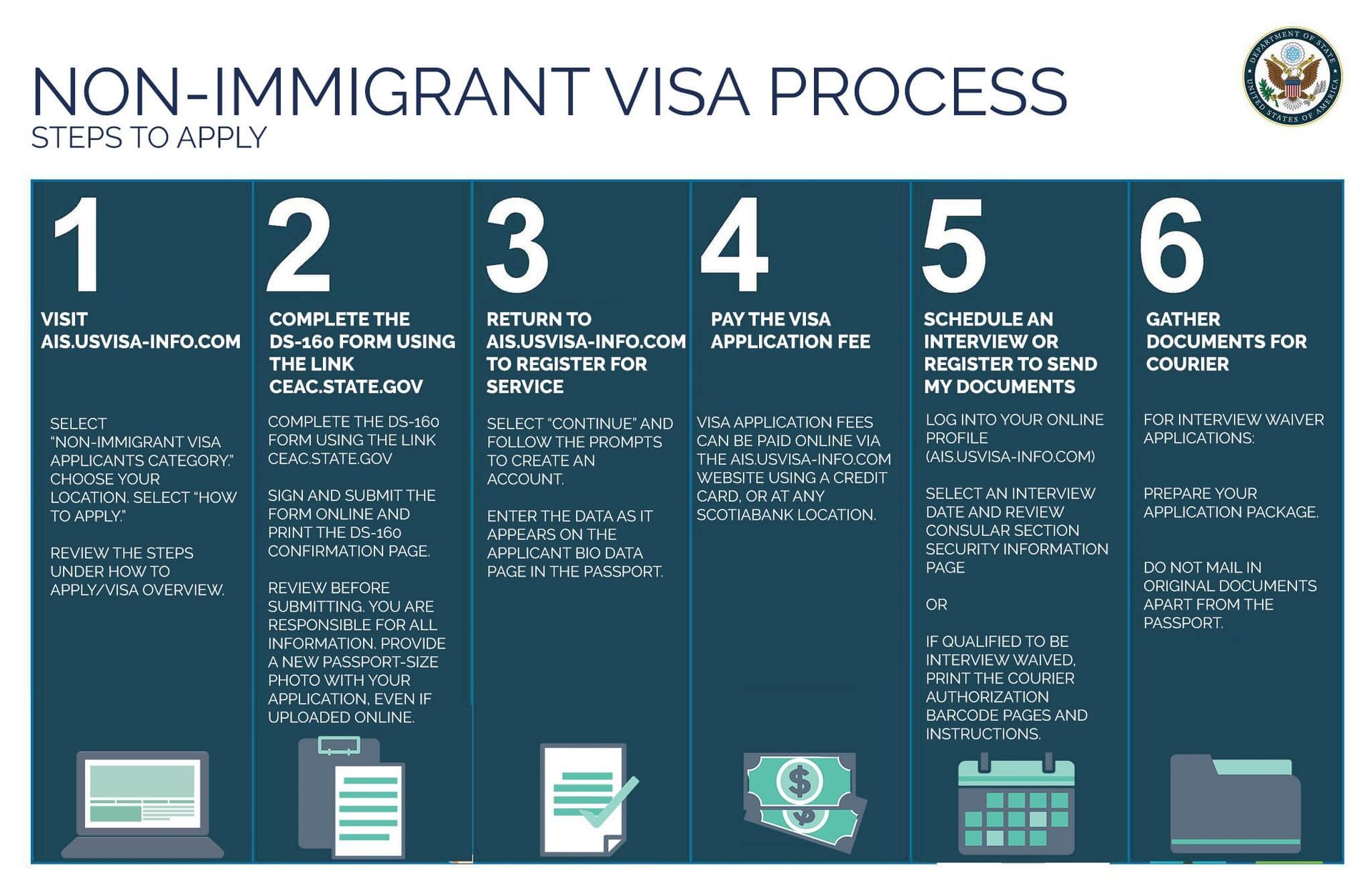
Step 1 – Petition Filing: The petitioner must file a Petition for Alien Relative (Form I-130) with USCIS to establish the family relationship and the petitioner's eligibility. For more details on the filing process, visit Filing Process Overview.
Step 2 – Permanent Residence Application: After I-130 approval, the beneficiary may apply for permanent residency through:
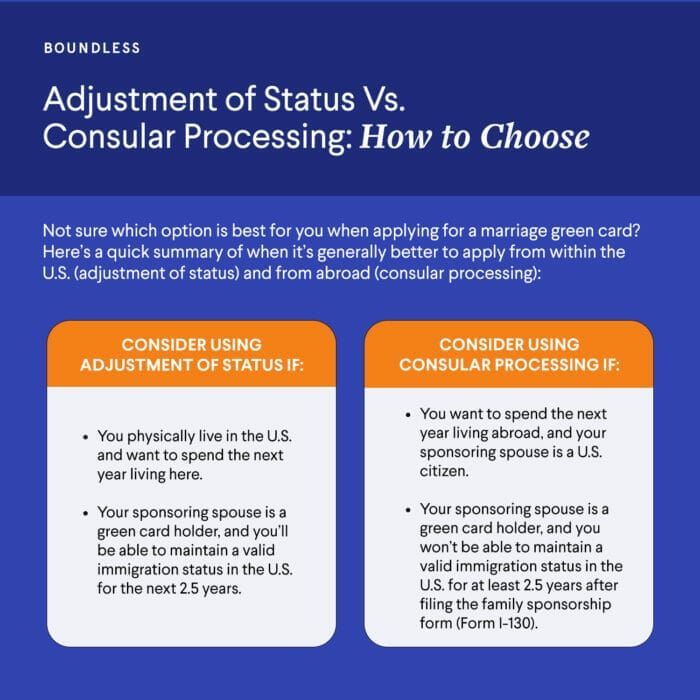
- Adjustment of Status (Form I-485): For beneficiaries already in the U.S.
- Immigrant Visa Application: For beneficiaries applying from overseas (For additional guidance on navigating visa processes, please refer to The Ultimate Guide to the Visa Application Process for the United States)
It's wise to note that filing fees are generally non-refundable, hence completeness in documentation before submitting is crucial. You can find more on this here.
Common Challenges and Tips for Streamlining
Some of the challenges in the filing process include:
- Documentation Gaps: Ensure all civil documents are authentic and translated into English, if necessary.
- Financial Requirements: Collect comprehensive financial documentation and consider acquiring a joint sponsor when necessary.
- Medical Examination Delays: Early scheduling for medical exams can prevent delays.
- Police Certificates: Start acquiring police certificates early as some processes may take time.
Navigating these challenges can make the immigration petition process smoother.
Immigration with Family: Considerations and Best Practices
Administrative Considerations
It’s essential to understand that separate petitions may be needed for each family member immigrating together. For instance, if a U.S. citizen sponsors both a spouse and a stepchild, individual I-130 petitions must be submitted for all beneficiaries. Explore more on this here.
Derivative Beneficiaries
In family preference categories, spouses and children of the primary beneficiary can often benefit from the primary beneficiary’s application. This allows some members to gain eligibility without needing separate petitions, streamlining the process further. You can read more about derivative beneficiaries here.
Emotional and Practical Preparation
As families navigate this process, here are some considerations:
- Maintain communication as the petition process can be lengthy.
- Prepare for emotional separations, as beneficiaries might need to remain abroad during application processing.
- Financial Planning: Coordination with sponsors is essential to meet support requirements.
- Thorough Documentation: Fully documenting family relationships is key to preventing complication requests from immigration authorities.
For additional guidance on selecting the right professional assistance, consider exploring Your Guide to Hiring the Best Immigration Lawyer in Columbus, Ohio.
Immigration to the United States Through Family Channels
In the U.S., family reunification remains a central tenet of immigration policy, demonstrating the country’s commitment to familial ties. It offers distinct advantages such as:
- Faster processing for immediate relatives with no caps
- Established legal frameworks for clear eligibility criteria
- Pathways to permanent residency and citizenship
- Rights to live and work in the U.S. once a Green Card is obtained
Current U.S. immigration services emphasize that family-based immigration remains the largest category of legal immigration, highlighting its critical role in shaping American society.
For an overview of the immigration policy regarding family channels, see Immigration Policy Overview.
Role of U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS)
The USCIS is the primary agency handling family immigration cases, offering numerous essential services:
- Official forms and instructions for petitions
- Fee schedules and payment methods
- Case status tracking to monitor petition progress
- Guidance documents on eligibility criteria and necessary documentation
Many applicants benefit from consulting experienced immigration attorneys or accredited representatives who can assist throughout the petition process. For expert legal guidance, please review Immigration Lawyer Dallas Texas: Expert Guidance for Overcoming Texas Immigration Challenges.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In summary, navigating family immigration can be a detailed but rewarding endeavor. Key points to remember include:
- Understanding eligibility criteria
- Familiarizing yourself with the immigration petition process
- A keen awareness of the distinct pathways available for family members
Next Steps for Consideration:
- Determine your eligibility - Verify if your relationship qualifies for immediate relatives or family preference categories.
- Gather necessary documentation - Collect all required documents, including civil, financial, and medical records.
- Consult professional guidance - Seek assistance from USCIS or immigration attorneys for tailored advice.
- File the I-130 petition - Submit your petition along with complete documentation and applicable fees.
- Monitor visa availability - Especially for family preference categories, ensuring you stay updated on priority dates.
- Prepare for the subsequent phase - After I-130 approval, ready yourself for adjustment of status or consular processing.
For personalized assistance, reaching out to USCIS resources or consulting qualified immigration professionals is recommended for tailored advice.
Becoming part of the American landscape through immigration to the United States is a journey filled with opportunities, and understanding the family immigration process is the first step to uniting with loved ones in the U.S.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is family immigration?
Family immigration refers to the processes through which U.S. citizens and lawful permanent residents can sponsor relatives for permanent residence in the United States.
How long does the family immigration process take?
The timeline can vary significantly based on the relationship category and whether the beneficiary is inside or outside the U.S., ranging from a few months to several years.
Can all family members be sponsored for immigration?
Not all family members qualify; only certain relatives may be sponsored, such as spouses, children, and siblings, depending on their relationship to the petitioner.
What documents are required for the I-130 petition?
Documents typically include proof of the petitioner's U.S. status, evidence of the family relationship, and financial documentation demonstrating ability to support the beneficiary.
Is legal assistance recommended for immigration cases?
Yes, legal assistance can help navigate complex immigration laws and processes, making it advisable to consult with an immigration attorney when possible.